近日,刘春刚教授团队在《Cell Death & Disease》杂志上发表了题为“GASC1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inhibiting the degradation of ROCK2”的论文。
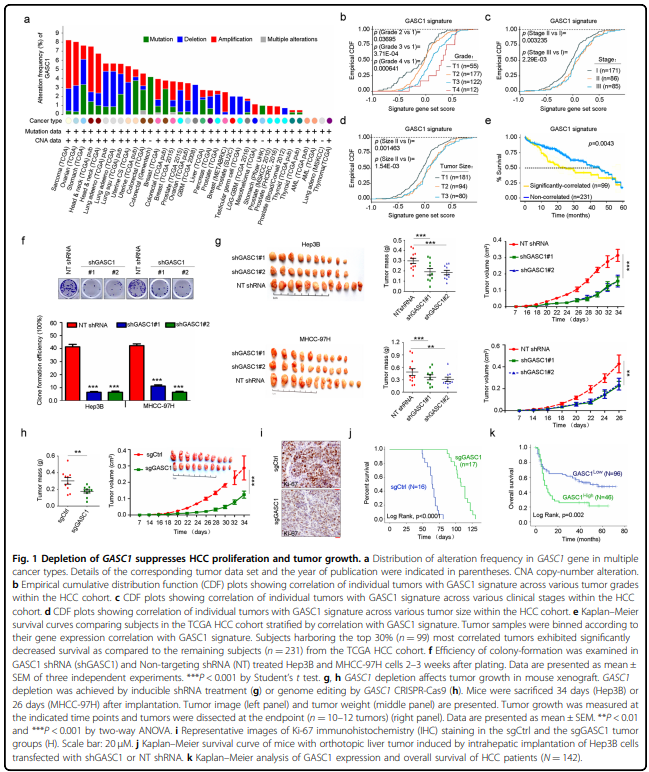
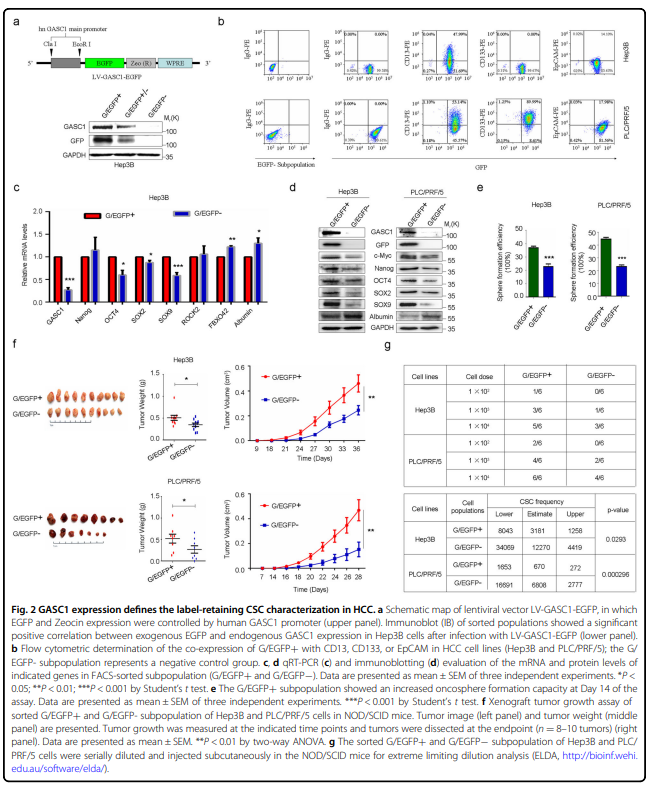
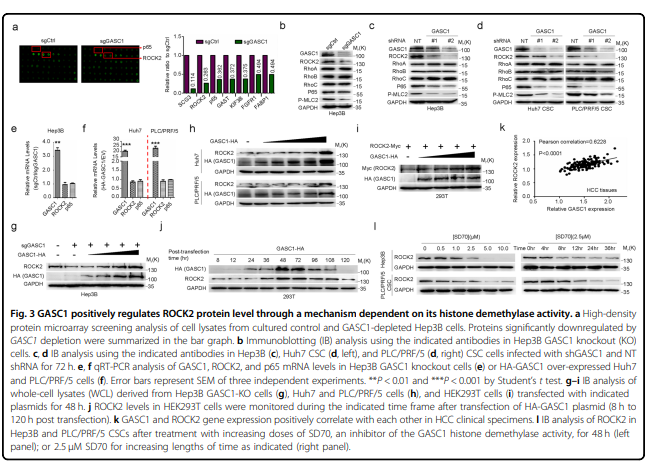
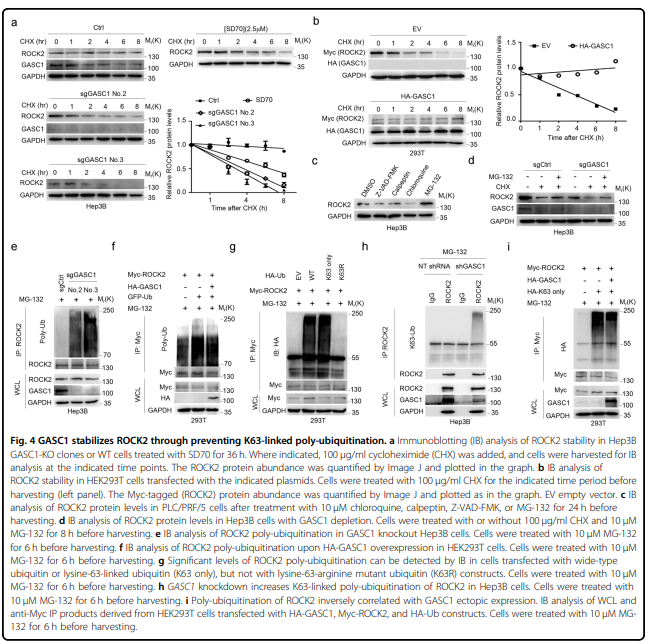
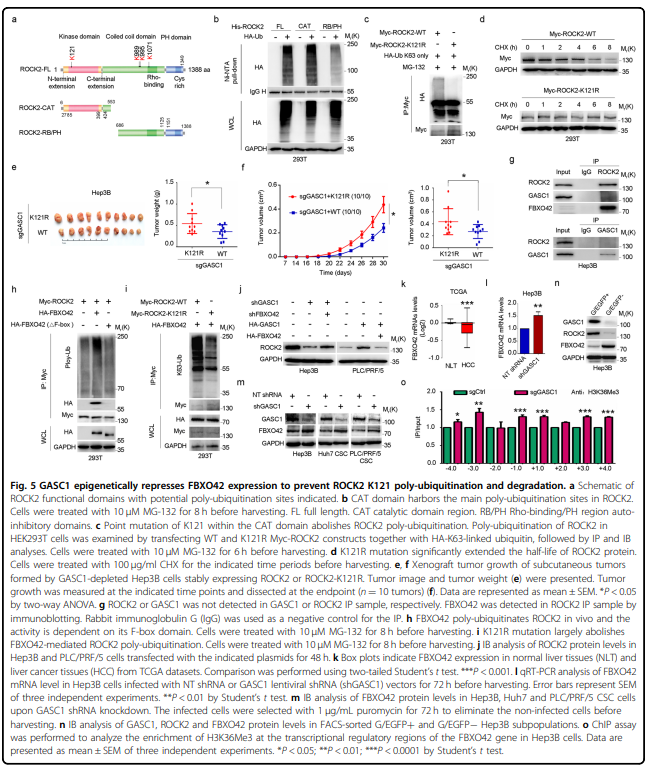
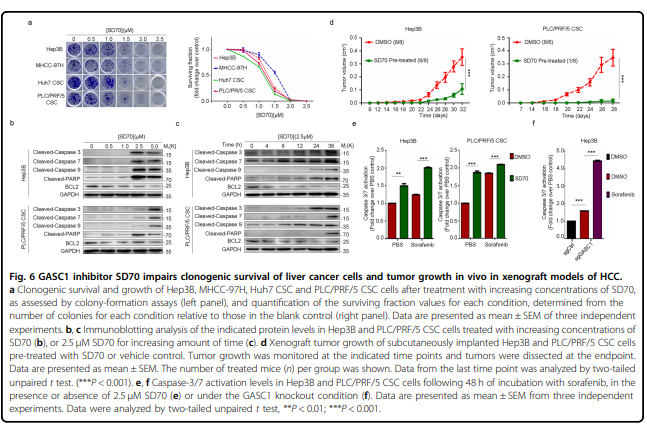
该研究发现组蛋白去甲基化酶GASC1特征与肝癌患者晚期肿瘤和较差的生存率相关。GASC1缺失导致肝癌细胞增殖和肿瘤生长减少。在HCC细胞群中观察到GASC1水平的明显异质性,预测其固有的高或低肿瘤启动能力。在机制上,GASC1参与调控Rho-GTPase信号通路的多个组分,包括其下游靶标ROCK2。GASC1去甲基酶活性保证了ROCK2蛋白泛素连接酶FBXO42的转录抑制,从而通过k63链接的多泛素化抑制了ROCK2的降解。用GASC1抑制剂SD70治疗可损害肝癌细胞株和小鼠异种移植瘤的生长,使它们对标准护理化疗敏感。
总体而言,这项工作确定了GASC1是肝癌中恶性细胞选择的靶点,GASC1特异性治疗为控制这种恶性肿瘤提供了有希望的新治疗方案。
GASC1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma
progression by inhibiting the degradation of
ROCK2
Na Shao, Jiamin Cheng , Hong Huang , Xiaoshan Gong , Yongling Lu , Muhammad Idris , Xu Peng ,
Belinda X. Ong , Qiongyi Zhang , Feng Xu and Chungang Liu
Shao et al. Cell Death and Disease (2021) 12:253
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-03550-w
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a devastating malignancy without targeted therapeutic options. Our results
indicated that the histone demethylase GASC1 signature is associated with later tumor stage and poorer survival in
HCC patients. GASC1 depletion led to diminished HCC proliferation and tumor growth. A distinct heterogeneity in
GASC1 levels was observed among HCC cell populations, predicting their inherent high or low tumor-initiating
capacity. Mechanistically, GASC1 is involved in the regulation of several components of the Rho-GTPase signaling
pathway including its downstream target ROCK2. GASC1 demethylase activity ensured the transcriptional repression of
FBXO42, a ROCK2 protein-ubiquitin ligase, thereby inhibiting ROCK2 degradation via K63-linked poly-ubiquitination.
Treatment with the GASC1 inhibitor SD70 impaired the growth of both HCC cell lines and xenografts in mice,
sensitizing them to standard-of-care chemotherapy. This work identifies GASC1 as a malignant-cell-selective target in
HCC, and GASC1-specific therapeutics represent promising candidates for new treatment options to control this
malignancy.