近日,汪凯、唐霓教授团队在《Cell Death & Disease》杂志上发表“Depletion of VPS35 attenuates metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by restraining the Wnt/PCP signaling pathway”的论文。
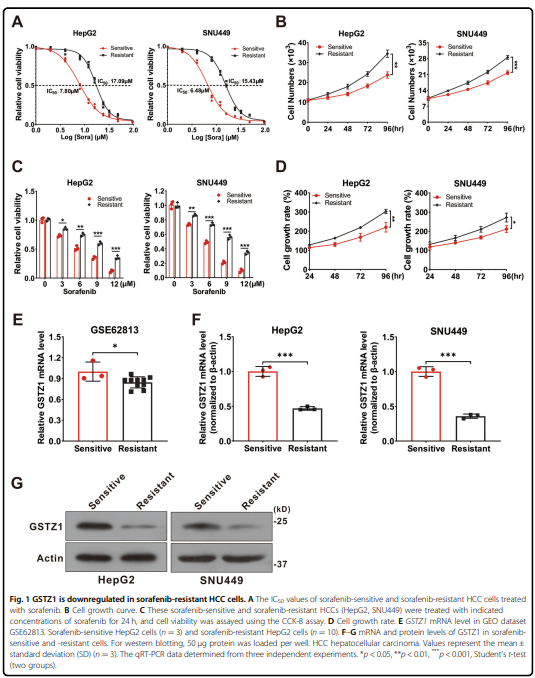
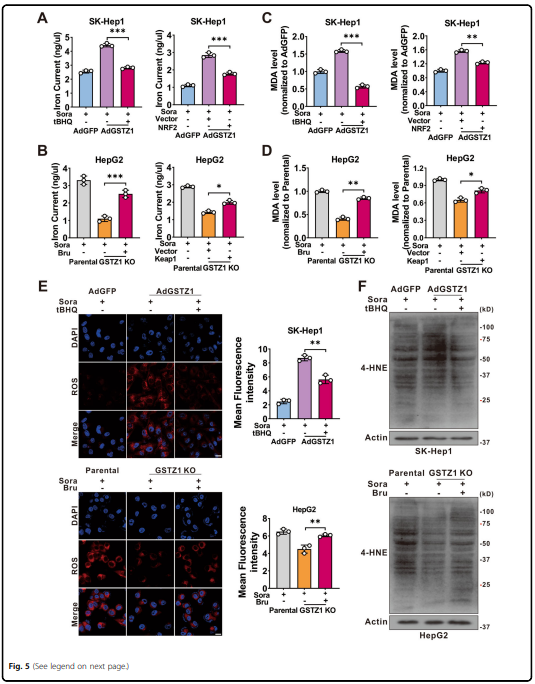
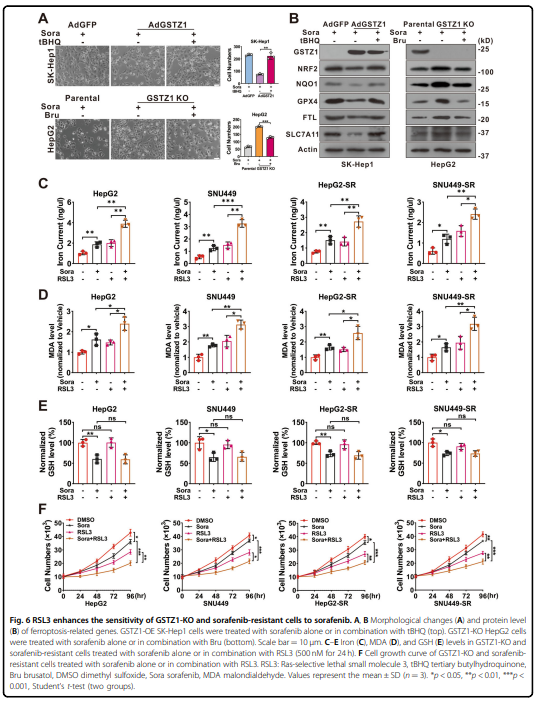
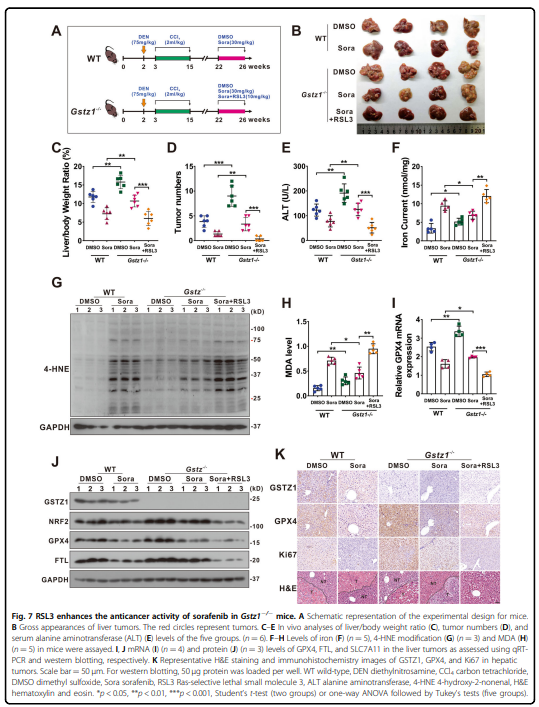
Sorafenib最初被鉴定为多种致癌激酶的抑制剂,已被证明在肝细胞癌(HCC)中诱导铁衰落。 然而,有些肝癌细胞系对索拉非尼诱导的铁致细胞死亡不敏感。谷胱甘肽s -转移酶zeta 1 (GSTZ1)是苯丙氨酸分解代谢的一种酶,它抑制了细胞氧化还原稳态核因子红系2相关因子2 (NRF2)的主调节因子的表达。 本研究旨在探讨GSTZ1在索拉非尼诱导的肝癌坏死中的作用及其分子机制。GSTZ1在索拉非尼耐药肝癌细胞中显著下调。 机制上,GSTZ1耗尽增强了NRF2通路的激活,增加了谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4 (GPX4)的水平,从而抑制索拉非尼诱导的铁衰弱。 索拉非尼与GPX4抑制剂RSL3联合使用,可显著抑制gstz1缺陷的细胞活力,促进铁衰弱,增加异位铁和脂质过氧化物。 在体内,索拉非尼联合RSL3对Gstz1 - / -小鼠HCC进展具有协同治疗作用。
综上所述,该研究表明GSTZ1通过抑制NRF2/GPX4轴增强索拉非尼诱导的肝癌细胞ferroptosis。 索拉非尼与GPX4抑制剂RSL3联合治疗HCC可能是一种有前景的治疗策略。
GSTZ1 sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib-induced ferroptosis via inhibition of NRF2/GPX4 axis
Qiujie Wang , Cheng Bin , Qiang Xue , Qingzhu Gao , Ailong Huang , Kai Wang and Ni Tang
Wang et al. Cell Death and Disease (2021) 12:426
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-03718-4
Abstract
Increasing evidence supports that ferroptosis plays an important role in tumor growth inhibition. Sorafenib, originally
identified as an inhibitor of multiple oncogenic kinases, has been shown to induce ferroptosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC). However, some hepatoma cell lines are less sensitive to sorafenib-induced ferroptotic cell death.
Glutathione S-transferase zeta 1 (GSTZ1), an enzyme in the catabolism of phenylalanine, suppresses the expression of
the master regulator of cellular redox homeostasis nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2). This study aimed
to investigate the role and underlying molecular mechanisms of GSTZ1 in sorafenib-induced ferroptosis in HCC. GSTZ1
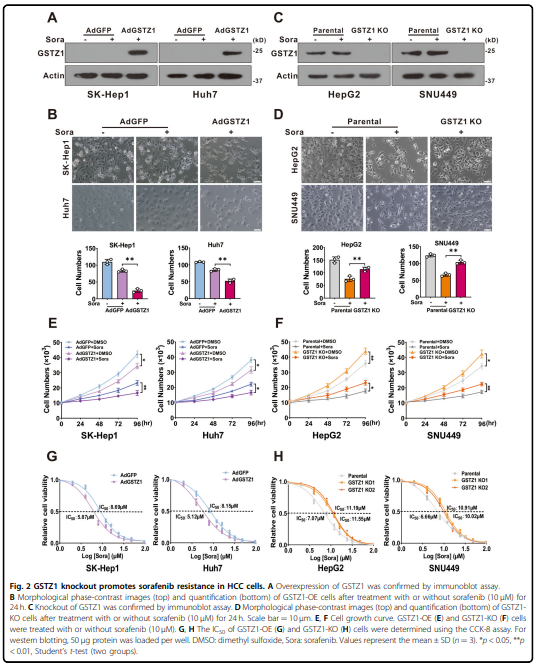
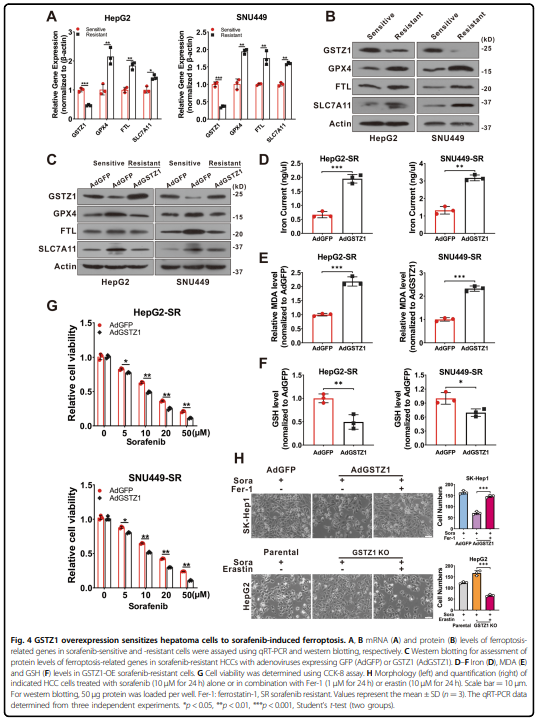
was significantly downregulated in sorafenib-resistant hepatoma cells. Mechanistically, GSTZ1 depletion enhanced the
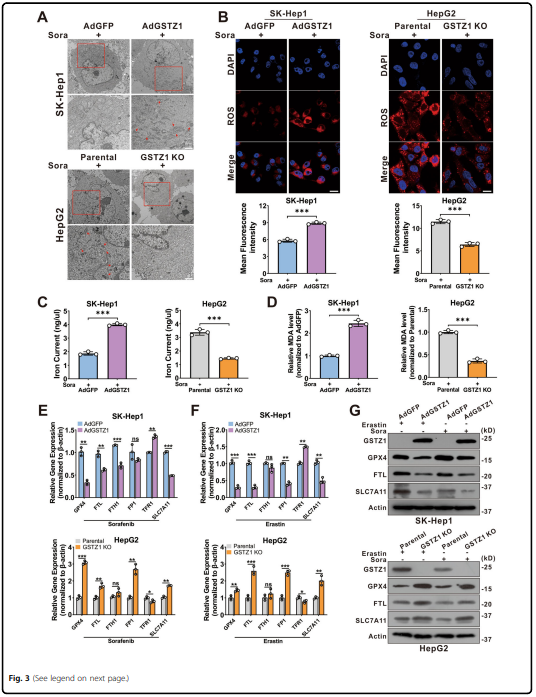
activation of the NRF2 pathway and increased the glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) level, thereby suppressing
sorafenib-induced ferroptosis. The combination of sorafenib and RSL3, a GPX4 inhibitor, significantly inhibited GSTZ1-
deficient cell viability and promoted ferroptosis and increased ectopic iron and lipid peroxides. In vivo, the
combination of sorafenib and RSL3 had a synergic therapeutic effect on HCC progression in Gstz1−/− mice. In
conclusion, this finding demonstrates that GSTZ1 enhanced sorafenib-induced ferroptosis by inhibiting the NRF2/
GPX4 axis in HCC cells. Combination therapy of sorafenib and GPX4 inhibitor RSL3 may be a promising strategy in HCC
treatment